Slope
Slope refers to the steepness or inclination of a land surface. It measures the rate of change in elevation over a horizontal distance. The slope is an essential topographic characteristic that helps describe the terrain's physical properties and influences various natural processes, such as water runoff, erosion, and land stability.
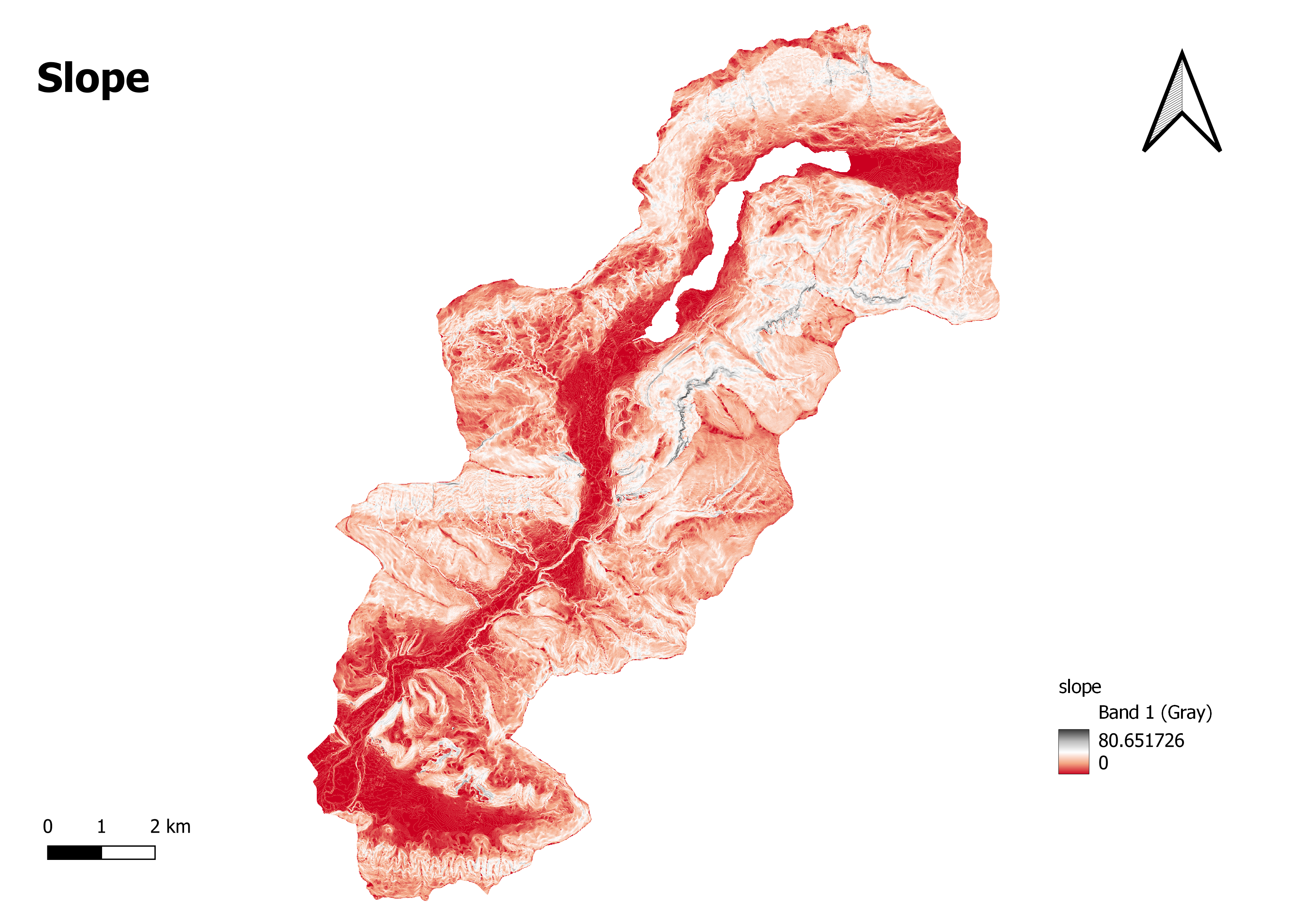
A slope map, also known as a slope gradient map, is a graphical representation that displays the distribution of slope values across a given area. It provides a visual depiction of the steepness or gentleness of the land surface. Slope maps are typically created using digital elevation models (DEMs) or topographic data. The slope values in a slope map are commonly represented using colors, shading, or contour lines.
The significance of the range in a slope map, especially the range between 0 (represented by the dark red colour) and 80.651726 (represented by the dark grey colour), may be interpreted as follows, with a colour gradient moving from red to white and finally to gray:
Deep Red: The value of 0, classified by the deep red color, represents areas with a flat or nearly flat terrain. These areas have minimal slope, indicating a gentle or level land surface.
Red to White: The range between deep red and white colors represents increasing slope values. As the color transitions from deep red to white, it signifies the gradual increase in slope steepness. The lighter shades of red represent moderately sloping areas, while the white color represents moderately steep slopes.
White to Gray: The transition from white to gray indicates the continuation of steep slopes beyond the moderately steep areas. The gray color represents the steepest slopes in the map.
Deep Gray: The value of 80.651726, classified by the deep gray color, represents areas with the steepest slopes. These areas have the highest slope values, indicating rugged terrain or steep landforms